The Phi-roots that are shown below can be approximated using many different methods. Two methods are possible using the information gleaned from the data below. One way is by using triangles (what I sometimes like to refer to as: "wedges") within regular polygons of odd numbers of sides. Each polygon is oriented with one of its sides along our visual-bottom putting one of its angles at its top. All of the triangles would then share their apex angle (the angle at their top) at the top of their surrounding polygon. Their bases would be shared along the polygon's base and along diagonals that horizontally cut across their associated polygon. The length of the base of each triangle is divided by the length of its slope. This makes each triangle's base equivalent to the f proportional value for that triangle while its slope is equal to the value of 1. Another way is to use trigonometry's sine function on one-half of each triangle's apex angle. From a few premises, is derived the formula:
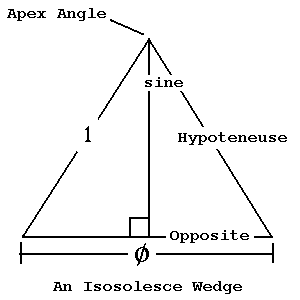 Opposite ÷ Hypoteneuse = sine (An_Angle_in_Radians)
Opposite ÷ Hypoteneuse = sine (An_Angle_in_Radians)
Hypoteneuse = 1 = Referencing Unit of Measurement
Opposite = sine (An_Angle_in_Radians)
Opposite = f ÷ 2
f ÷ 2 = sine (An_Angle_in_Radians)
f ÷ 2 = sine (2p ´ (An_Angle_in_Degrees° ÷ 360°))
An_Angle_in_Degrees = Apex_Angle° ÷ 2
f ÷ 2 = sine (2p ´ Apex_Angle° ÷ 2 ÷ 360°)
f ÷ 2 = sine (p ´ Apex_Angle° ÷ 360°)
f = 2 ´ sine (p ´ Apex_Angle° ÷ 360)
Additionally, every other result must be signed negative or else its resulting polynomial
won't have integer coefficients.
Additionally, every other result must be signed negative or else its resulting polynomial won't have integer coefficients.
The following output is from a Perl program (61 Kb) that I
updated on Thursday, 10 October 2002.
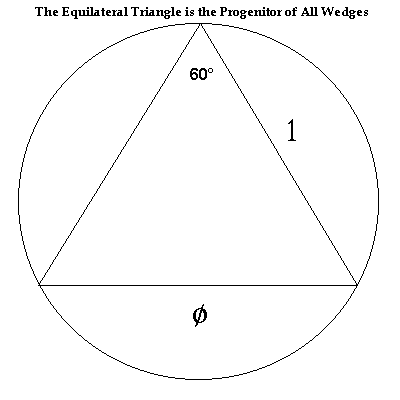
Prime 3-Gon, TotAng = 180° The circumferencial angle is 60°
| 1. Angle is 60° | its Sine is | f = ± 1 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 1 |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial
®
If 0 loosely equals zero,
then this test proves positive.
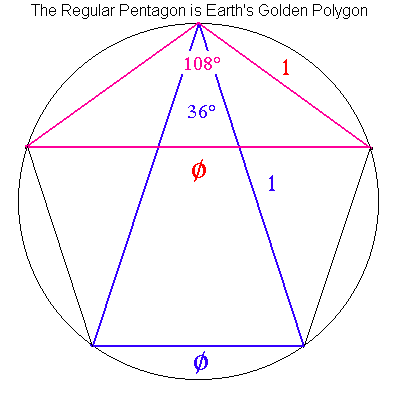
Prime 5-Gon, TotAng = 540° The circumferencial angle is 108°
| 1. Angle is 36° | its Sine is | f = ± 0.618033989 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 1.618033989 |
| 2. Angle is 108° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial
®
If 0 loosely equals zero,
then this test proves positive.
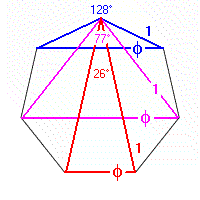
Prime 7-Gon, TotAng = 900° The circumferencial angle is 128.5714285714°
| 1. Angle is 25 5/7° | its Sine is | f = ± 0.445041868 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 2.246979604 |
| 2. Angle is 77 1/7° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 3. Angle is 128 4/7° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.801937736 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.554958132 |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial
®
If 0 loosely equals zero,
then this test proves positive.
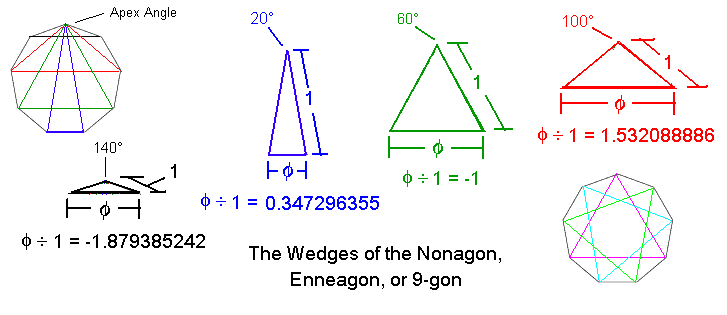
Composite 9-Gon, TotAng = 1260° The circumferencial angle is 140°
The 9-Gon has its own unique roots, plus those of the:
3-Gon.
| 1. Angle is 20° | its Sine is | f = ± 0.347296355 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 2.879385242 |
| 2. Angle is 60° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 3. Angle is 100° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.532088886 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.652703645 |
| 4. Angle is 140° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial
®
If -1.11022302462516e-016 loosely equals zero,
then this test proves positive.
Prime 11-Gon, TotAng = 1620° The circumferencial angle is 147.2727272727°
| 1. Angle is 16 4/11° | its Sine is | f = ± 0.284629677 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 3.513337092 |
| 2. Angle is 49 1/11° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 3. Angle is 81 9/11° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.309721468 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.763521118 |
| 4. Angle is 114 6/11° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 5. Angle is 147 3/11° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.918985947 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.521108558 |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial ® If -4.9960036108132e-015 loosely equals zero, then this test proves positive.
Prime 13-Gon, TotAng = 1980° The circumferencial angle is 152.3076923076°
| 1. Angle is 13 11/13° | its Sine is | f = ± 0.241073361 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 4.148114905 |
| 2. Angle is 41 7/13° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 3. Angle is 69 3/13° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.136129493 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.880181358 |
| 4. Angle is 96 12/13° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 5. Angle is 124 8/13° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.770912051 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.564680781 |
| 6. Angle is 152 4/13° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial ® If -5.55111512312578e-015 loosely equals zero, then this test proves positive.
Composite 15-Gon, TotAng = 2340° The circumferencial angle is 156°
The 15-Gon has its own unique roots, plus those of the: 3-Gon, and 5-Gon.
| 1. Angle is 12° | its Sine is | f = ± 0.209056927 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 4.783386117 |
| 2. Angle is 36° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 3. Angle is 60° | its Sine is | f = ± 1 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 1 |
| 4. Angle is 84° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 5. Angle is 108° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.618033989 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.618033989 |
| 6. Angle is 132° | its Sine is |
f = | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f |
= |
| 7. Angle is 156° | its Sine is | f = ± 1.956295201 | its Reciprocal is 1 ÷ f | = ± 0.511170297 |
Its Polynomial of All f Roots is
Its Reciprocal Polynomial of All Reciprocal f Roots is
Test result for this polynomial ® If -2.63122856836162e-014 loosely equals zero, then this test proves positive.
If the test result is a number in scientific
notation showing some absolute value less than
10 decimal digits, then this isn't too bad.
In fact, it's pretty good since this program
rounds to 10 digits.
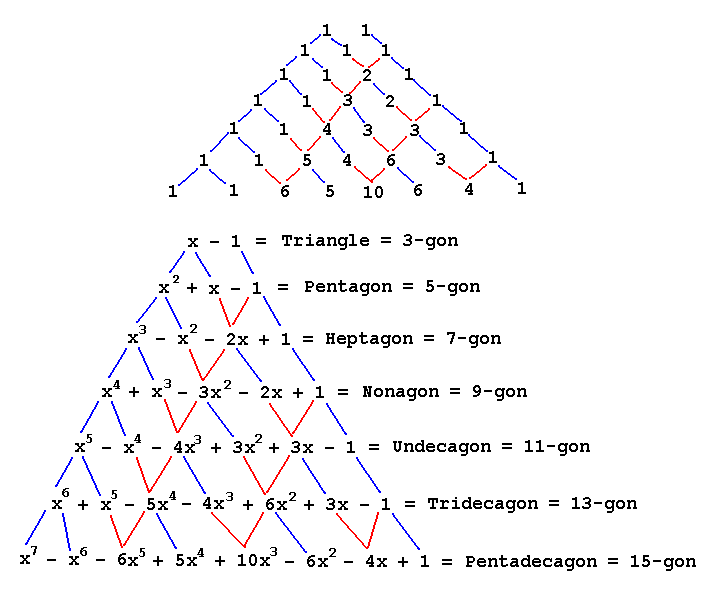
There is a short-cut for determining the coefficients. They form a convenient pyramid. Some coefficients, represented by the blue lines, are carried down from above. The others, represented by the red lines, are summed up:
Next Lesson: Fermat-Primed Polygons
| GCD || Golden || Averaging || Comment || Odd || Fermat || Salt || Refs || Terms |
| Book || Essays || Links || Posts || Donations || Home |
http://vinyasi.mayashastra.org/book/odd-sided_polygons.shtml
Thursday, 10 October 2002 10:04:36 Pacific Daylight Time